Context
The Arctic is the Earth's region that lies North of the 66° 34' parallel. Geographically, it expands over multiple countries, including Canada, Finland, Denmark (through Greenland), Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States (through Alaska). It is, therefore, an ocean surrounded by land, mainly composed of water that freezes over the cold months and melts over the warm months.
Together with its geographic opposite, the Antarctic, the Arctic has a fundamental role in global climate stabilisation. On the one hand, its white surface is able to radiate most of the incoming solar radiation back into space, therefore reflecting part of the Sun's heat. On the other, the Arctic tundra stores immense quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) that would otherwise contribute to further global warming. Additionally, the Arctic holds last reservoirs of freshwater, stored in its glaciers and icebergs.
With regard to climate change, the Arctic is an area of extreme vulnerability. Temperatures are rising twice to three times as fast compared to the global average, in a process that is commonly referred to as Arctic amplification. When sea ice melts, it leaves land and ocean surfaces uncovered which, due to their darker colour, absorb heat and accelerate further ice loss.
These are the articles written by me for OsservatorioArtico, an Italian online newspaper centered around the Arctic region
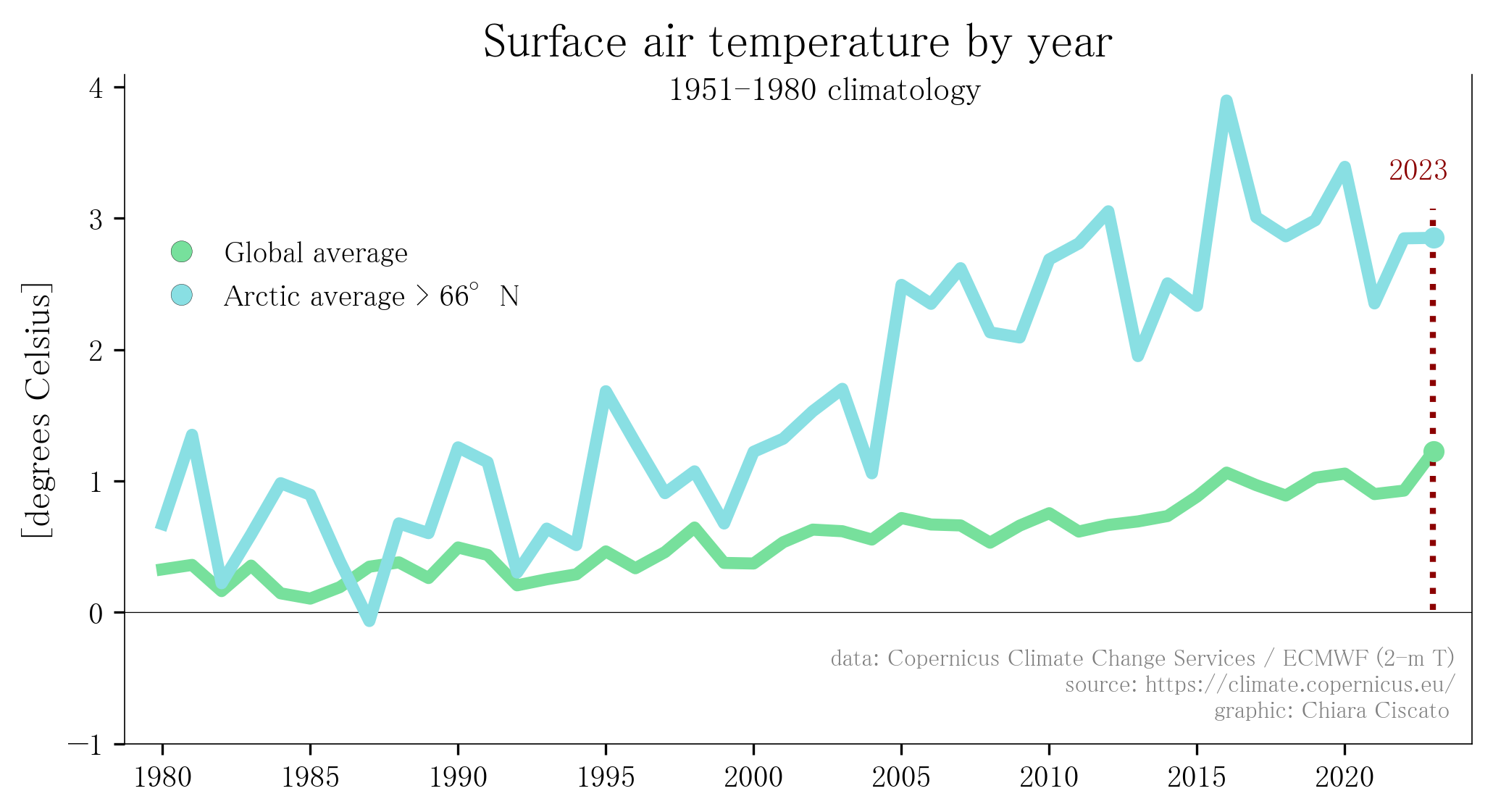 Arctic Amplification
Arctic Amplification
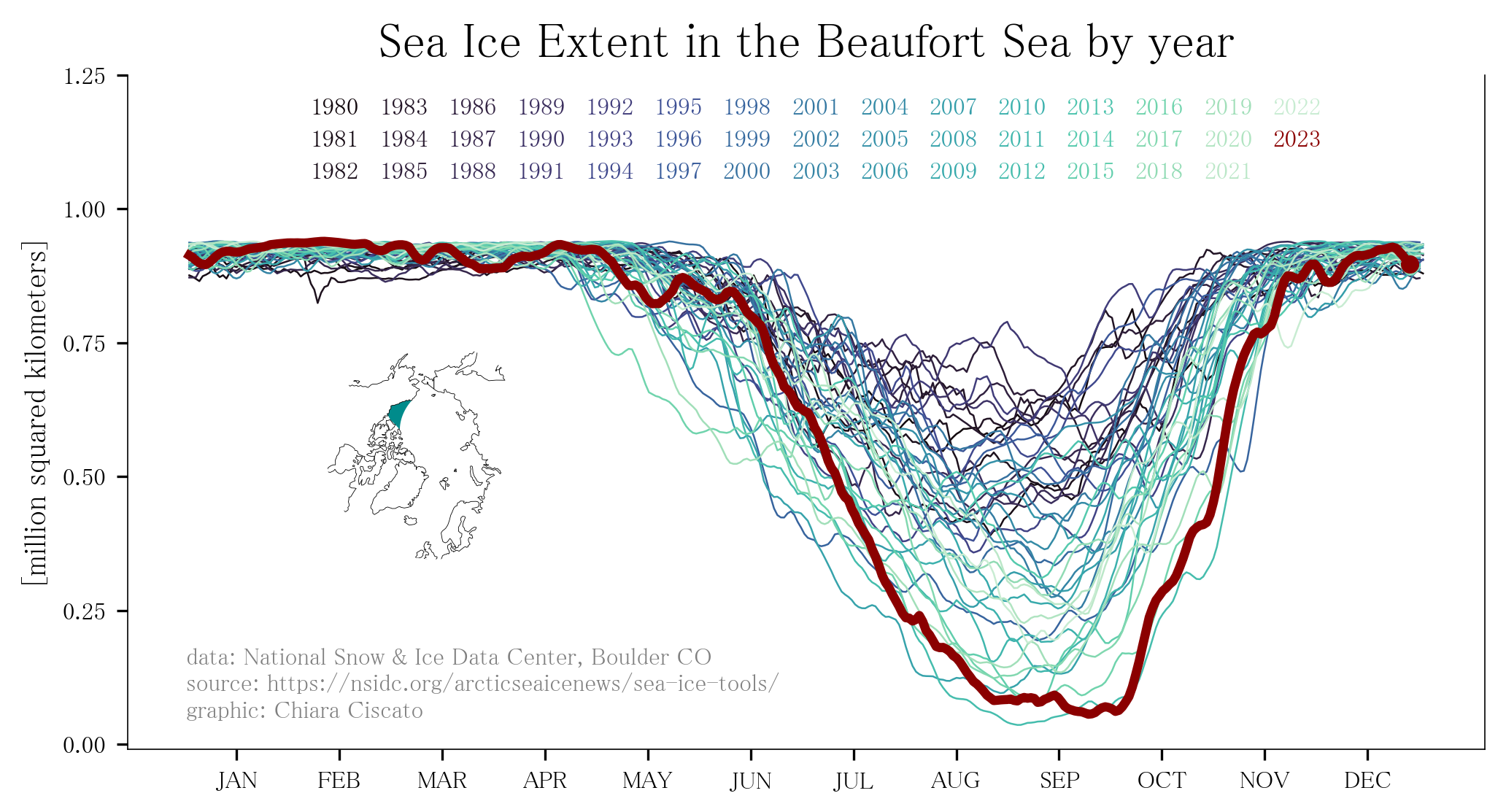 The Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea
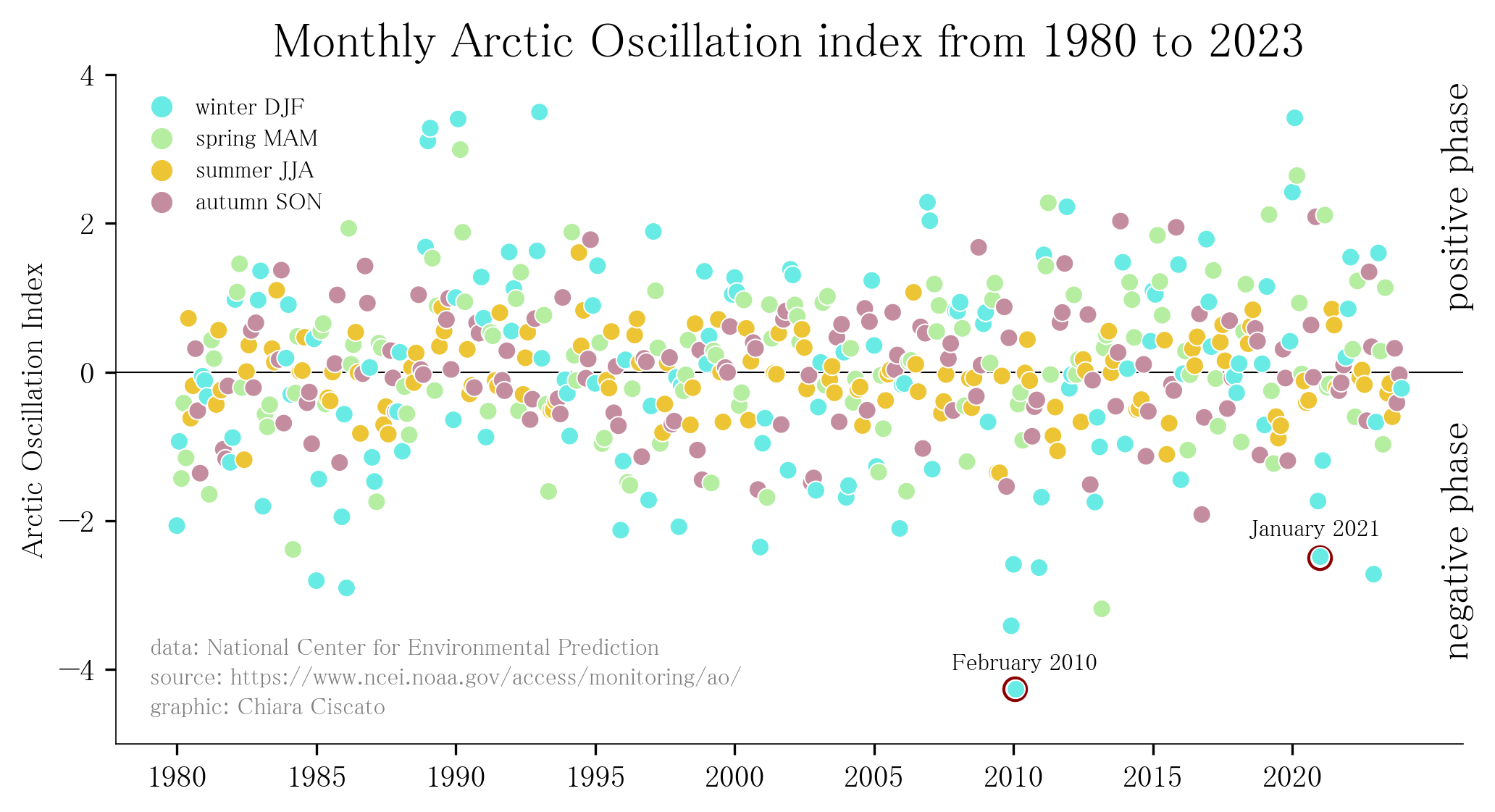 Arctic Oscillation
Arctic Oscillation
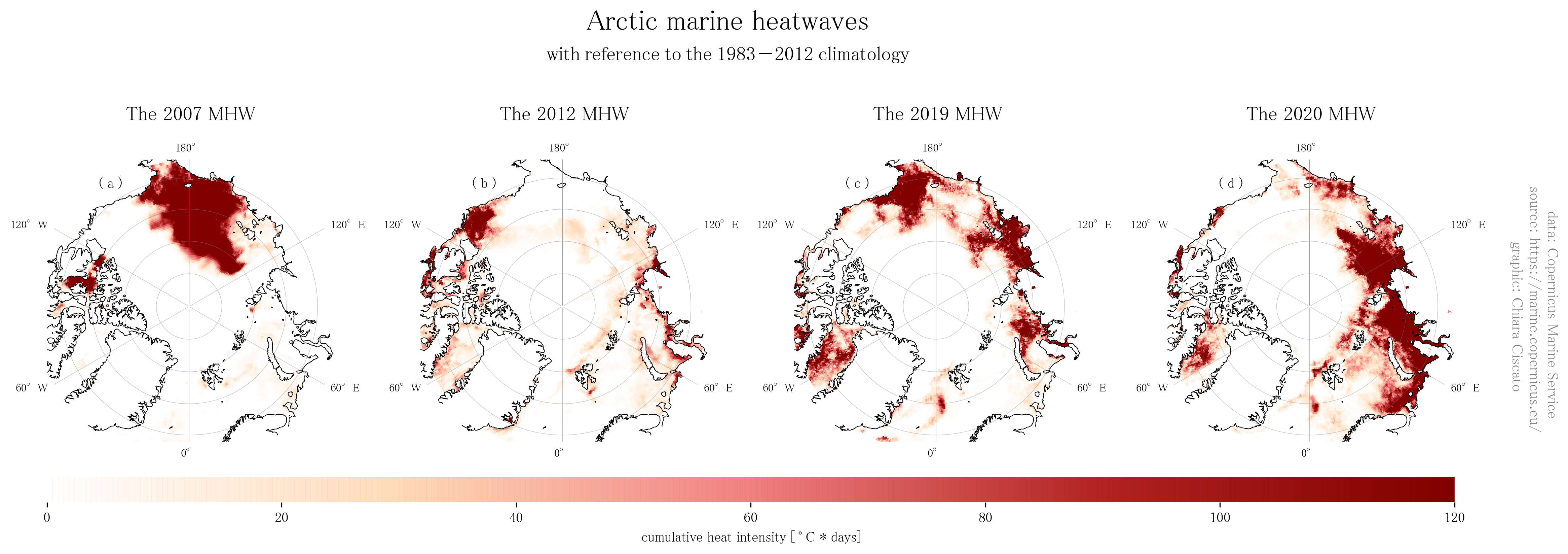 Arctic marine heatwaves
Arctic marine heatwaves
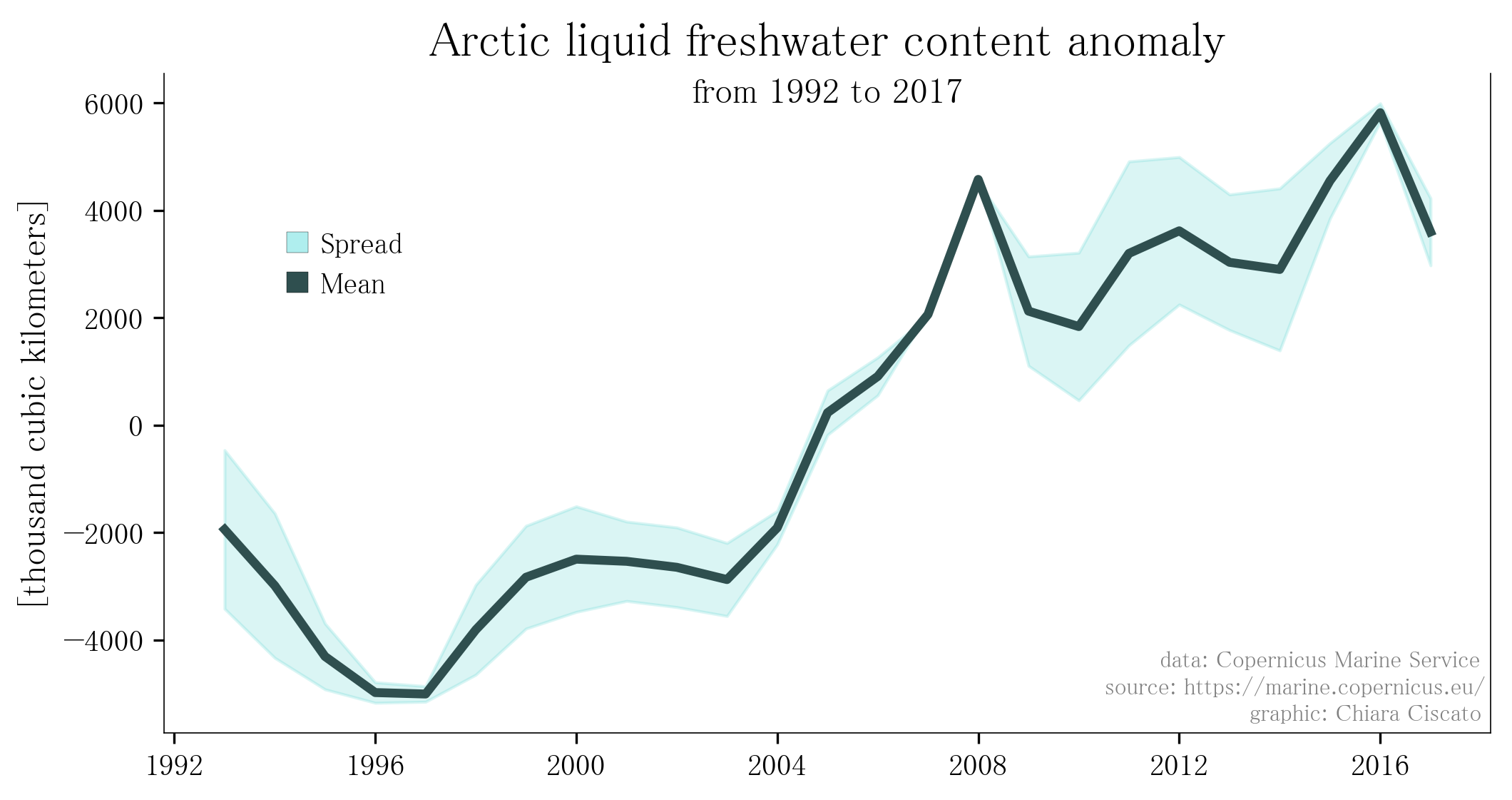 Arctic Atlantification
Arctic Atlantification